Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Section Review 7-1
Humans are fabricated upwardly of trillions of cells — the basic unit of measurement of life on globe. In this article, we explain some of the structures found in cells and depict a few of the many types of cell found in our bodies.
Cells can be thought of as tiny packages that comprise minute factories, warehouses, transport systems, and power plants. They function on their ain, creating their own energy and self-replicating — the jail cell is the smallest unit of life that can replicate.
Withal, cells also communicate with each other and connect to create a solid, well stuck-together creature. Cells build tissues, which course organs; and organs work together to keep the organism alive.
Robert Hook commencement discovered cells in 1665. He gave them their proper noun because they resembled the cella (Latin for "small rooms") where monks lived in monasteries.
Different cell types can await wildly unlike, and carry out very different roles within the trunk.
For instance, a sperm cell resembles a tadpole, a female egg cell is spherical, and nerve cells are substantially sparse tubes.
Despite their differences, they frequently share certain structures; these are referred to every bit organelles (mini-organs). Below are some of the near of import:
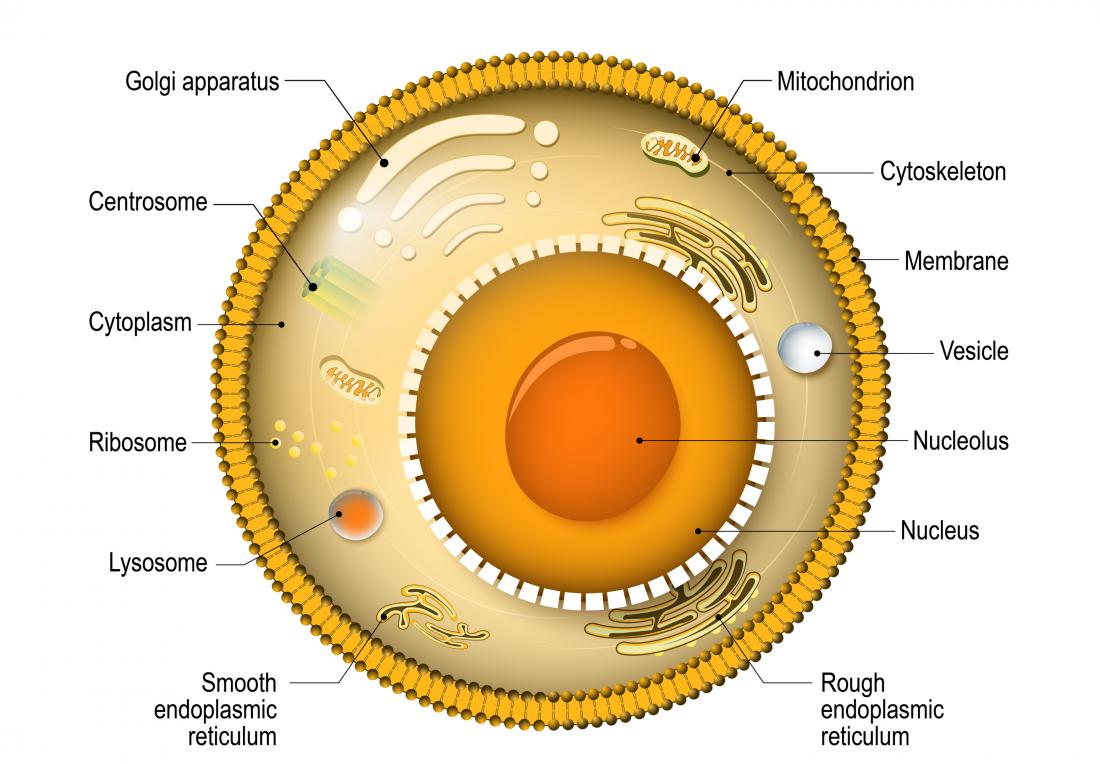
A simplified diagram of a homo cell.
Nucleus
The nucleus can exist idea of as the jail cell'due south headquarters. In that location is normally ane nucleus per cell, but this is not always the case, skeletal muscle cells, for instance, have 2. The nucleus contains the majority of the jail cell's Deoxyribonucleic acid (a small amount is housed in the mitochondria, encounter below). The nucleus sends out messages to tell the cell to grow, dissever, or die.
The nucleus is separated from the rest of the cell past a membrane called the nuclear envelope; nuclear pores inside the membrane permit through small molecules and ions, while larger molecules need transport proteins to help them through.
Plasma membrane
To ensure each cell remains separate from its neighbor, information technology is enveloped in a special membrane known as the plasma membrane. This membrane is predominantly fabricated of phospholipids, which prevent h2o-based substances from entering the cell. The plasma membrane contains a range of receptors, which carry out a number of tasks, including beingness:
- Gatekeepers: Some receptors allow sure molecules through and stop others.
- Markers: These receptors deed every bit name badges, informing the immune system that they are part of the organism and not a foreign invader.
- Communicators: Some receptors help the prison cell communicate with other cells and the environment.
- Fasteners: Some receptors help bind the jail cell to its neighbors.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the interior of the cell that surrounds the nucleus and is effectually 80 pct water; information technology includes the organelles and a jelly-like fluid called the cytosol. Many of the important reactions that take place in the cell occur in the cytoplasm.
Lysosomes and peroxisomes
Both lysosomes and peroxisomes are essentially bags of enzymes. Lysosomes contain enzymes that break downwardly big molecules, including old parts of the cells and foreign material. Peroxisomes contain enzymes that destroy toxic materials, including peroxide.
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton can be considered the scaffolding of the cell. It helps it maintain the correct shape. However, different regular scaffolding, the cytoskeleton is flexible; it plays a role in cell division and cell movement — the power of some cells to move, such as sperm cells, for case.
The cytoskeleton also helps in cell signaling through its interest in the uptake of fabric from outside the cell (endocytosis) and is involved in moving materials around inside the cell.
Endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) processes molecules within the jail cell and helps transport them to their last destinations. In detail, it synthesizes, folds, modifies, and transports proteins.
The ER is made up of elongated sacs, chosen cisternae, held together by the cytoskeleton. There are two types: rough ER and polish ER.
Golgi apparatus
Once molecules have been processed by the ER, they travel to the Golgi apparatus. The Golgi appliance is sometimes considered the post office of the prison cell, where items are packaged and labeled. Once materials go out, they may be used inside the cell or taken outside of the jail cell for use elsewhere.
Mitochondria
Oftentimes referred to as the powerhouse of the cell, mitochondria help turn energy from the food that we eat into energy that the cell can use — adenosine triphosphate (ATP). However, mitochondria have a number of other jobs, including calcium storage and a part in cell expiry (apoptosis).
Ribosomes
In the nucleus, DNA is transcribed into RNA (ribonucleic acrid), a molecule like to Dna, which carries the same message. Ribosomes read the RNA and interpret it into poly peptide by sticking together amino acids in the guild defined by the RNA.
Some ribosomes float freely in the cytoplasm; others are attached to the ER.
Our trunk is constantly replacing cells. Cells need to divide for a number of reasons, including the growth of an organism and to fill gaps left by expressionless and destroyed cells afterwards an injury, for case.
There are two types of cell division: Mitosis and meiosis.
Mitosis
Mitosis is how nigh of the cells in the trunk divide. The "parent" cell splits into two "daughter" cells.
Both daughter cells take the same chromosomes as each other and the parent. They are referred to equally diploid because they have two complete copies of the chromosomes.
Meiosis
Meiosis creates sexual activity cells, such as the male sperm and female person egg cells. In meiosis, a modest portion of each chromosome breaks off and sticks to another chromosome; this is chosen genetic recombination.
This means that each of the new cells has a unique set of genetic information. It is this process that allows genetic diversity to occur.
So, in brief, mitosis helps us grow, and meiosis makes sure nosotros are all unique.
When you consider the complexity of the man body, it is no surprise that there are hundreds of different types of prison cell. Below is a small selection of homo cell types:
Stalk cells
Stem cells are cells that are nevertheless to cull what they are going to become. Some differentiate to become a certain jail cell type, and others dissever to produce more stalk cells. They are found in both the embryo and some developed tissues, such as os marrow.
Os cells
There are at to the lowest degree three primary types of os cell:
- Osteoclasts, which dissolve os.
- Osteoblasts, which class new bone.
- Osteocytes, which are surrounded past bone and assistance communicate with other os cells.
Blood cells
There are three major types of claret cell:
- red blood cells, which comport oxygen around the body
- white blood cells, which are role of the immune system
- platelets, which assistance claret clot to prevent blood loss after injury
Muscle cells
Likewise called myocytes, muscle cells are long, tubular cells. Muscle cells are important for a huge range of functions, including move, support, and internal functions, such as peristalsis — the move of food forth the gut.
Sperm cells
These tadpole-shaped cells are the smallest in the human trunk.
They are motile, significant that they can motility. They accomplish this movement past using their tail (flagellum), which is packed with free energy-giving mitochondria.
Sperm cells cannot divide; they just carry ane copy of each chromosome (haploid), unlike the bulk of cells, which deport two copies (diploid).
Female egg cell
Compared with the sperm cell, the female egg jail cell is a giant; it is the largest human being cell. The egg cell is also haploid and so that the Deoxyribonucleic acid from the sperm and egg tin combine to create a diploid cell.
Fatty cells
Fat cells are likewise called adipocytes and are the main constituent in adipose tissue. They contain stored fats called triglycerides that can be used as energy when needed. Once the triglycerides are used upward, the fatty cells shrink. Adipocytes also produce some hormones.
Nerve cells
Nerves cells are the communication organization of the body. As well called neurons, they consist of two major parts — the cell trunk and nerve processes. The central trunk contains the nucleus and other organelles, and the nerve processes (axons or dendrites) run like long fingers, carrying messages far and wide. Some of these axons can be over one meter long.
Cells are as fascinating equally they are varied. In i sense they are autonomous cities that function alone, producing their own free energy and proteins; in some other sense, they are role of the huge network of cells that creates tissues, organs, and us.
Source: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320878
Post a Comment for "Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Section Review 7-1"